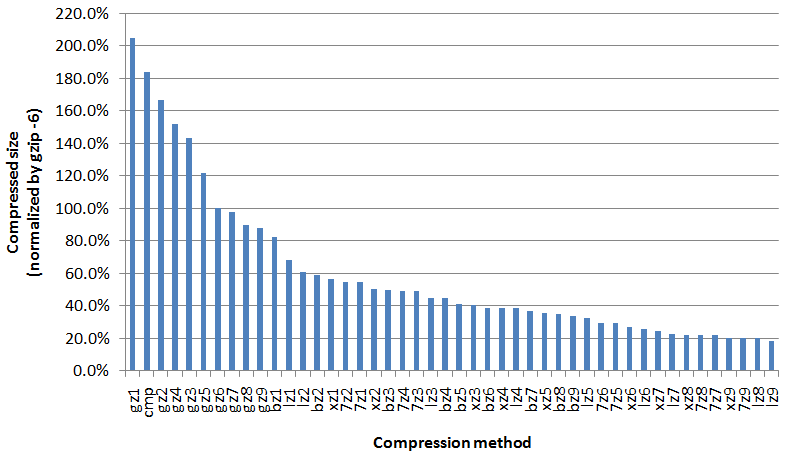
The
quantity of retained data is growing at a rate causing distress at
technology centers. While only part of a solution, better compression
methods are needed. The graph below shows compression of a 174.7
GiB tar file (my raw PhD research results) relative to the default gzip
compression (gzip -6). The following are the shorthand names for the
compression methods. The trailing number in the graph labels, where
present, represents the preset level of compression. E.g. gz9 is
equivalent to 'gzip -9'. (The compression program zip (
Info-zip)
3.0 was not included due to the default compression method being
effectively identical to gzip.) Final size of the lzip -9 results: 1.4
GiB.
lz =
lzip 1.10
xz =
xz 4.999.9beta
gz =
gzip 1.3.13
cmp =
compress 4.2.4
bz =
bzip2 1.0.5
The compression by lzip has an impressive advantage over gzip but at the
expense of time. The compression times where not recorded, but it would
be interesting to plot to show realtive cost of compression. In some
cases, the compression may be seen as a one time event while disk space
is an on-going expense. In some cases decompression time may be more of a
concern.
A much more complete comparison of compression methods can be found at
MaximumCompression.